For the first time, new images from the James Webb Space Telescope have revealed galaxies with stellar bars at a time when the universe was a quarter of its present age.
Stellar bars are elongated features of stars that stretch from the centers of galaxies into their outer disks. They funnel gas into central regions, boosting star formation.
In a release, the University of Texas said the find of the barred galaxies will require scientists to fine-tune their theories of galaxy evolution, and noted that the Hubble Space Telescope had never detected bars at such young epochs.
For example, while the galaxy EGS-23205 appears blurry in a Hubble image, the image from Webb is more defined, revealing a spiral galaxy with a clear stellar bar.
ON THIS DAY IN HISTORY, JAN. 7, 1610, GALILEO DISCOVERS THE MOONS OF JUPITER
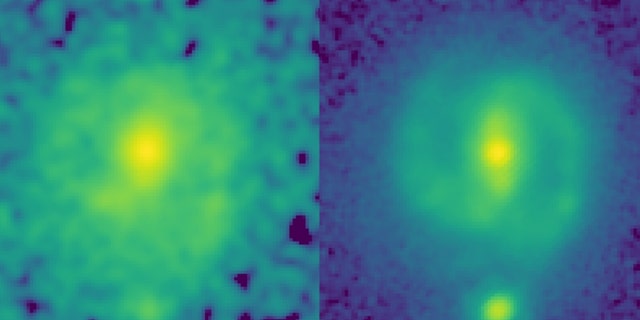
The power of JWST to map galaxies at high resolution and at longer infrared wavelengths than Hubble allows it look through dust and unveil the underlying structure and mass of distant galaxies. This can be seen in these two images of the galaxy EGS23205, seen as it was about 11 billion years ago. In the HST image (left, taken in the near-infrared filter), the galaxy is little more than a disk-shaped smudge obscured by dust and impacted by the glare of young stars, but in the corresponding JWST mid-infrared image (taken this past summer), it’s a beautiful spiral galaxy with a clear stellar bar.
(Credit: NASA/CEERS/University of Texas at Austin)
The James Webb Space Telescope has a larger mirror, giving it more light-gathering ability and allowing it to see farther with higher resolution.
As it observes longer infrared wavelengths than Hubble, it can also see through dust better.
“I took one look at these data, and I said, ‘We are dropping everything else!’” Shardha Jogee, professor of astronomy at The University of Texas at Austin, said in a statement, describing data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (CEERS).

Ball Aerospace lead optical test engineer Dave Chaney inspects six primary mirror segments, critical elements of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, prior to cryogenic testing in the X-ray & Cryogenic Facility at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala.
(Credit: NASA/MSFC/David Higginbotham)
Another barred galaxy, EGS-24268, is also from about 11 billion years ago – making two barred galaxies existing farther back in time than previously discovered.
GREEN COMET WILL PASS BY EARTH FOR FIRST TIME SINCE NEANDERTHALS ROAMED EARTH
The international group of researchers highlighted these galaxies and showed examples of four others from more than 8 billion years ago in an article in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
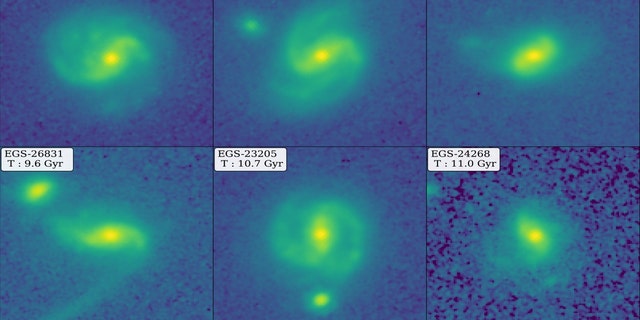
Montage of JWST images showing six example barred galaxies, two of which represent the highest lookback times quantitatively identified and characterized to date. The labels in the top left of each figure show the lookback time of each galaxy, ranging from 8.4 to 11 billion years ago (Gyr), when the universe was a mere 40% to 20% of its present age.
(Credit: NASA/CEERS/University of Texas at Austin)
Two undergraduate students played a key role by visually reviewing hundreds of galaxies and searching for those that could be analyzed with a more stringent mathematical approach.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
Bars also aid in the formation of supermassive black holes in the centers of galaxies, channeling the gas part of the way.
The existence of these bars, the university said, challenges theoretical models, and the team will be testing different models in additional work.
“This discovery of early bars means galaxy evolution models now have a new pathway via bars to accelerate the production of new stars at early epochs,” Jogee said.
